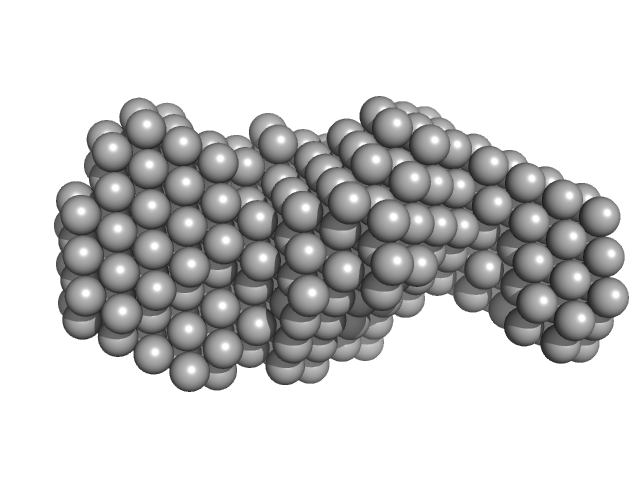
|
Synchrotron SAXS
data from solutions of
Probable S-adenosyl-L-methionine-dependent RNA methyltransferase RSM22, mitochondrial-monomer
in
40 mM Tris pH 7.5, 500 mM NaCl, 5% glycerol, 2.5 mM DTT, pH 7.5
were collected
on the
B21 beam line
at the Diamond Light Source storage ring
(Didcot, UK)
using a Pilatus 2M detector
at a sample-detector distance of 4 m and
at a wavelength of λ = 0.1 nm
(I(s) vs s, where s = 4πsinθ/λ, and 2θ is the scattering angle).
One solute concentration of 2.90 mg/ml was measured
at 25°C.
120 successive
3 second frames were collected.
The data were normalized to the intensity of the transmitted beam and radially averaged; the scattering of the solvent-blank was subtracted.
Rsm22 was purified in 40mM Tris pH7.5, 500mM NaCl, 5% Glycerol, 2.5mM DTT for SAXS purpose. Batch mode SAXS studies were carried out on the purified Rsm22 at B21 beamline of Diamond Light Source (DLS), UK. 40 µL of Rsm22 sample was used and 120 frames were collected. Scattered X-rays at a wavelength of 0.1 nm (at 12.4 keV) were recorded with a Pilatus 2M detector. The buffer scatterings were subtracted from protein scatterings using the program SCATTER (Reference: Förster, S., Apostol, L. and Bras, W. (2010)) and PRIMUS (Reference: Konarev, P. V., (2003)). The radius of gyration Rg, forward scattering I0, the maximum dimensions Dmax and the interatomic distance distribution functions P(r) were estimated using the GNOM package (Reference: Svergun, D. I. (1992)) in SCATTER and PRIMUS. The ab initio models of Rsm22 were generated by DAMMIN of the online-SAXS cluster at EMBL, Hamburg (Reference: D. I. Svergun (1999)) using the output file from GNOM package.
|
|
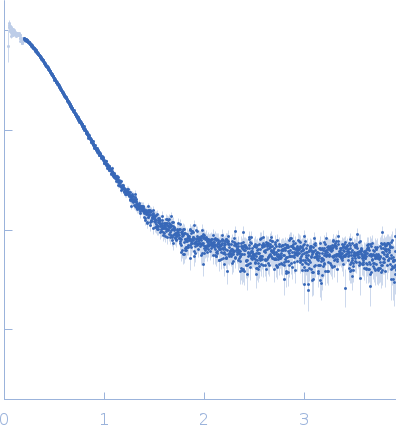 s, nm-1
s, nm-1