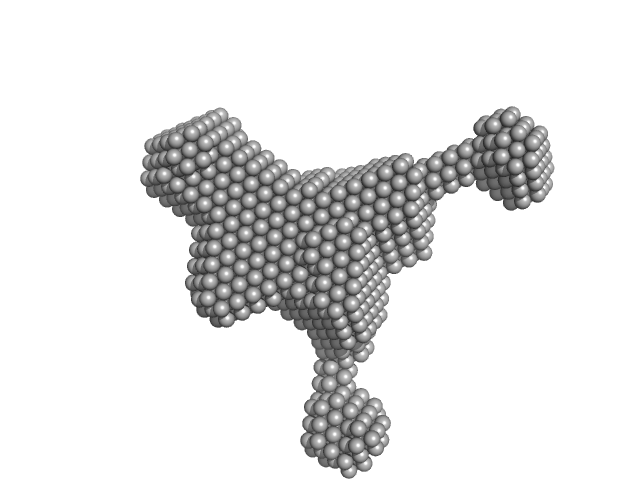
|
Synchrotron SAXS data from solutions of ASO2 DNA in the presence of target RNA in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4 were collected on the B21 beam line at the Diamond Light Source (Didcot, UK) using a Eiger 4M detector at a sample-detector distance of 0.4 m and at a wavelength of λ = 0.09537 nm (I(s) vs s, where s = 4πsinθ/λ, and 2θ is the scattering angle). 18 successive 180 second frames were collected from a sample at 15°C. The data were normalized to the intensity of the transmitted beam and radially averaged; the scattering of the solvent-blank was subtracted.
Concentration: UNKNOWN
|
|
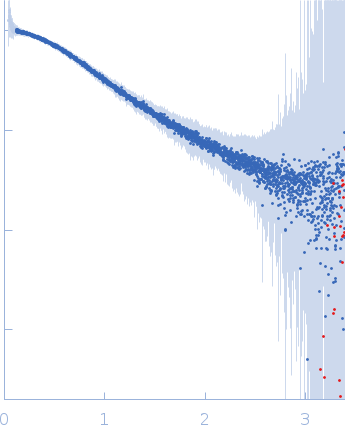 s, nm-1
s, nm-1
