|
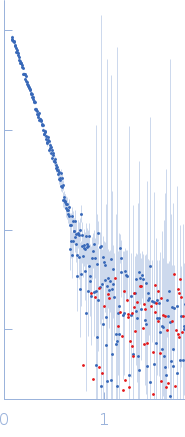
SAXS data from solutions of chloroplast FOF1-ATP synthase from Spinacia oleracea in 150 mM NaCl, 30 mM HEPES, 2 mM MgCl2, 0.04% (w/v) tPCC-α-M, pH 8 were collected using a Rigaku MicroMax 007-HF instrument at the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (MIPT; Dolgoprudny, Russian Federation) equipped with a Multiwire gas-filled ASM DTR Triton 200 detector at a sample-detector distance of 2 m and at a wavelength of λ = 0.154 nm (I(s) vs s, where s = 4πsinθ/λ, and 2θ is the scattering angle). One solute concentration of 5.00 mg/ml was measured at 20°C. One 5400 second frame was collected. The data were normalized to the intensity of the transmitted beam and radially averaged; the scattering of the solvent-blank was subtracted.
The protein of study is a chloroplast FOF1-ATP synthase (cFOF1) from Spinacia oleracea solubilized in 0.04% (w/v) 4-trans-(4-trans-Propylcyclohexyl)-cyclohexyl α-maltoside (tPCC-α-M). SAXS data confirm that cFOF1 purified by anion-exchange chromatography and incubated at 150 mM NaCl is a mixture of monomers and dimers with approximate volume fractions 27% and 73%, respectively. Dimers are formed by F1/F1 contacts (presumably via δ-subunit).
|
|
 s, nm-1
s, nm-1
![Static model image ATP synthase subunit alpha, chloroplastic ATP synthase subunit beta, chloroplastic ATP synthase gamma chain, chloroplastic ATP synthase delta chain, chloroplastic ATP synthase epsilon chain, chloroplastic ATP synthase subunit a, chloroplastic ATP synthase subunit b, chloroplastic ATP synthase subunit b', chloroplastic ATP synthase subunit c, chloroplastic 4-trans-(4-trans-Propylcyclohexyl)-cyclohexyl α-maltoside OTHER [STATIC IMAGE] model](/media//pdb_file/SASDRS8_fit1_model1.png)