The structure and stability of the disulfide-linked γS-crystallin dimer provide insight into oxidation products associated with lens cataract formation.
Thorn DC,
Grosas AB,
Mabbitt PD,
Ray NJ,
Jackson CJ,
Carver JA
J Mol Biol
(2018 Dec 12)
|
|
|
|

|
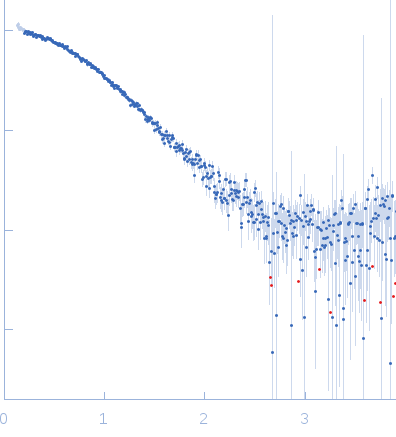
| Sample: |
Gamma-crystallin S dimer, 42 kDa Homo sapiens protein
|
| Buffer: |
20 mM sodium phosphate, pH: 7 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at Bruker Nanostar II, Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation/Australian Centre for Neutron Scattering on 2018 Feb 23
|
|
| RgGuinier |
2.4 |
nm |
| Dmax |
7.5 |
nm |
| VolumePorod |
45 |
nm3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
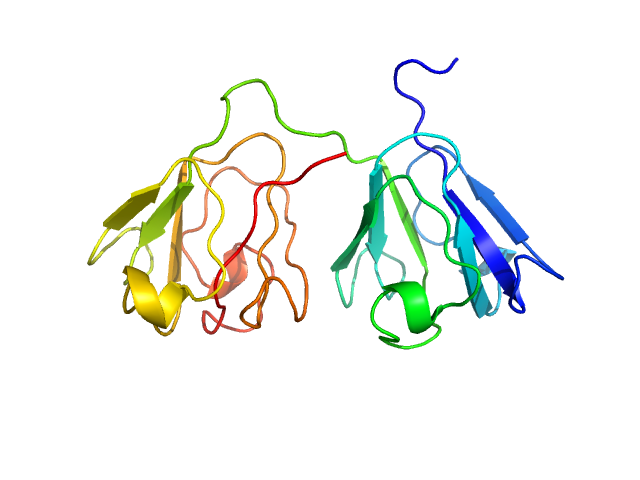
| Sample: |
Gamma-crystallin S monomer, 21 kDa Homo sapiens protein
|
| Buffer: |
20 mM sodium phosphate, pH: 7 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at Bruker Nanostar II, Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation/Australian Centre for Neutron Scattering on 2018 Feb 23
|
|
| RgGuinier |
1.8 |
nm |
| Dmax |
5.9 |
nm |
| VolumePorod |
27 |
nm3 |
|
|