c-di-AMP hydrolysis by a novel type of phosphodiesterase promotes differentiation of multicellular bacteria
Latoscha A,
Drexler D,
Al-Bassam M,
Kaever V,
Findlay K,
Witte G,
Tschowri N
(2019 Oct 01)
doi: 10.1101/789354
|
Submitted to SASBDB: 2020 Jan 16
Published in SASBDB:
|
|
|
|
|
|
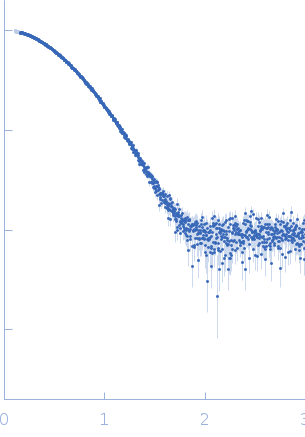
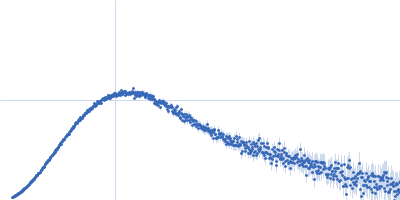
| Sample: |
Alkaline phosphodiesterase I or Nucleotide pyrophosphatase monomer, 46 kDa Streptomyces venezuelae protein
|
| Buffer: |
20 mM HEPES, 200mM NaCl, pH: 7.5 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at EMBL P12, PETRA III on 2018 May 17
|
|
| RgGuinier |
2.4 |
nm |
| Dmax |
7.8 |
nm |
| VolumePorod |
74 |
nm3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Sample: |
Cyclic di-AMP binding protein (Putative regulatory, ligand-binding protein) dimer, 38 kDa Streptomyces venezuelae protein
|
| Buffer: |
200 mM NaCl, 30 mM NaPi, 5% (v/v) glycerol, pH: 6.5 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at EMBL P12, PETRA III on 2019 Nov 4
|
|
| RgGuinier |
2.8 |
nm |
| Dmax |
9.2 |
nm |
| VolumePorod |
69 |
nm3 |
|
|